Table Of Content

While it’s true that each approach has its own modus operandi, there is also significant overlap. After prototyping comes user testing, but it’s important to note that this is rarely the end of the Design Thinking process. In reality, the results of the testing phase will often lead you back to a previous step, providing the insights you need to redefine the original problem statement or to come up with new ideas you hadn’t thought of before.
Challenges of Design Thinking
The Rise of the Design Thinking Movement and its Relation to Architecture - ArchDaily
The Rise of the Design Thinking Movement and its Relation to Architecture.
Posted: Wed, 19 Jan 2022 08:00:00 GMT [source]
Discover how this step, often a tipping point, emphasizes small-scale applications to gauge real-world viability. Whether paper prototyping or small-scale implementation, this phase is the cornerstone of the brainstorming process. You can use the design thinking process to get more people involved, and help everyone contribute ideas.
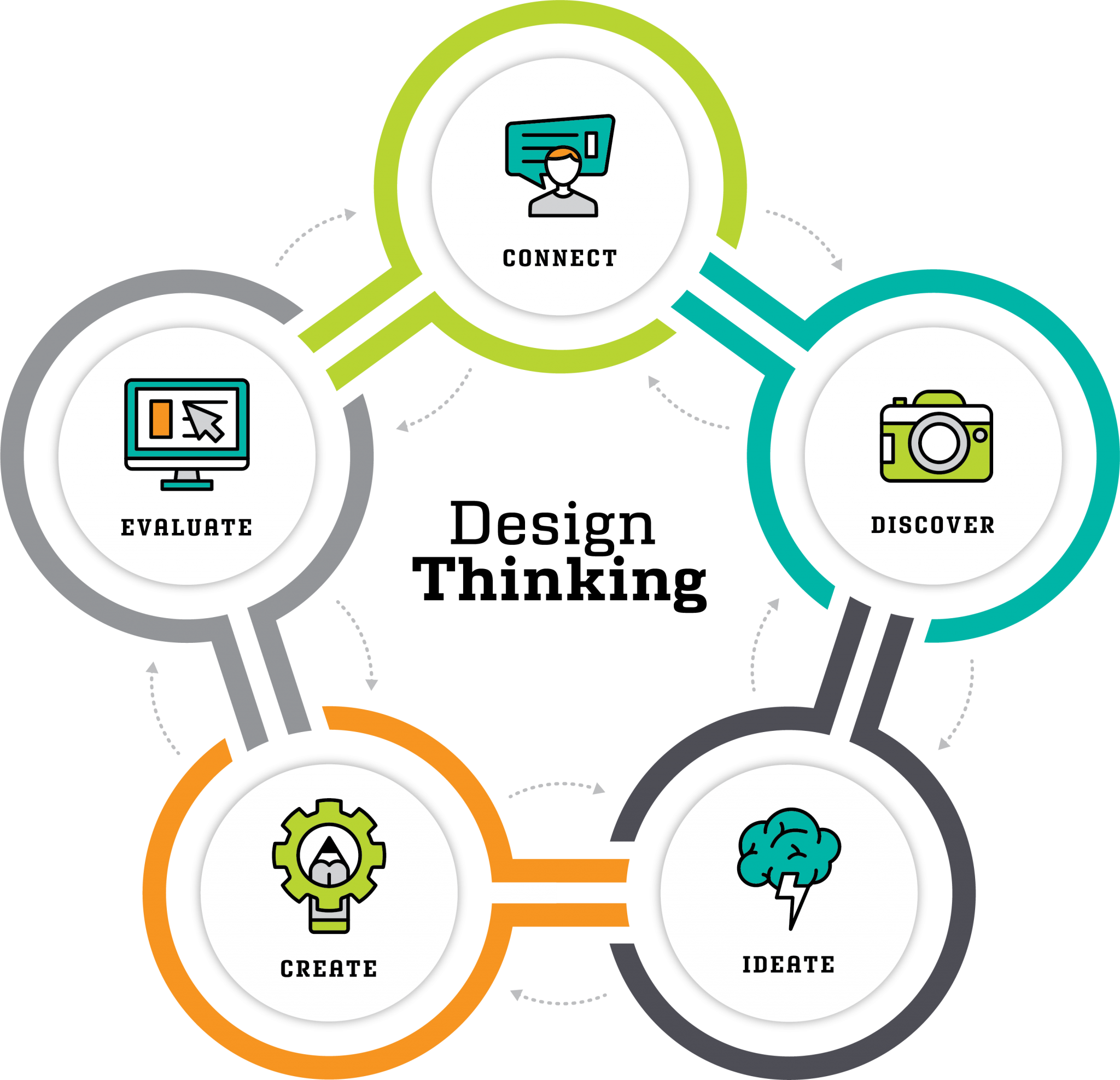
What are the 5 Stages of the Design Thinking Process
Steve Eppinger is a professor of management science and innovation at MIT Sloan. He holds the General Motors Leaders for Global Operations Chair and has a PhD from MIT in engineering. He is the faculty co-director of MIT's System Design and Management program and Integrated Design and Management program, both master’s degrees joint between the MIT Sloan and Engineering schools. His research focuses on product development and technical project management, and has been applied to improving complex engineering processes in many industries. Explore our online course Design Thinking and Innovation to discover how to leverage fundamental design thinking principles and innovative problem-solving tools to address business challenges. In order for this approach to be adopted across large organizations, it needed to be standardized.
Related UX Design Articles
You can also pursue an online course or workshop that dives deeper into design thinking methodology. This can be a practical path if you want to improve your design thinking skills or require a more collaborative environment. You might consider developing your communication, innovation, leadership, research, and management skills, as those are often listed alongside design thinking in job postings and professional profiles. If you want to learn design thinking, take an active role in your education.
Implementation and prototyping
Design thinking is an iterative process — it’s not something you do once and call it done. For organizations who’ve never run a design thinking workshop before, it can feel like a big change in how you approach the design process. Simply put, design thinking is a working process, while human-centered design is a mindset or approach. Your priority here is to generate as many ideas as possible, without judging or evaluating them. This step encourages designers to think creatively and push the boundaries of what's possible.
Solution-focused thinking
At the same time, design thinking is all about getting hands-on; the aim is to turn your ideas into tangible, testable products or processes as quickly as possible. Designers or evaluators rigorously test the complete product using the best solutions identified in the Prototype stage. This is the final stage of the five-stage model; however, in an iterative process such as design thinking, the results generated are often used to redefine one or more further problems. You can then proceed with further iterations and make alterations and refinements to rule out alternative solutions. The ultimate goal is to get as deep an understanding of the product and its users as possible.
Tech Talks: Increase Your Competitive Edge through Design Thinking - Reach Further
Tech Talks: Increase Your Competitive Edge through Design Thinking.
Posted: Wed, 07 Feb 2018 08:00:00 GMT [source]
Stage II: Define
Design thinking is an iterative, non-linear process which focuses on a collaboration between designers and users. It brings innovative solutions to life based on how real users think, feel and behave. In the “Implement” phase, the team brings these ideas to life through prototypes. The team tests, iterates and refines these ideas based on user feedback. This stage is crucial for translating abstract concepts into tangible, viable products, services, or experiences. Now, armed with a well-defined problem, the design thinking process enters the ideation stage—a veritable playground for creative brainstorming.
Learn more about Design Thinking (DT)
If the MIT-Altitude team studying walkers had ended user involvement after its initial interviews, it would likely have ended up with a walker that didn’t work very well for customers. Design Thinking is characterized by its collaborative and iterative nature, emphasizing creativity, empathy, and experimentation. It encourages a bias towards action and a willingness to embrace ambiguity and failure as part of the innovation process. By focusing on understanding user needs and rapidly iterating through prototyping and testing, Design Thinking enables teams to develop solutions that are more effective, user-centered, and impactful. Another increasingly popular method of applying design thinking is through design thinking workshops.
Resetting Our Mental Boxes and Developing a Fresh Mindset
Design thinking reverses this process and advocates that teams begin with desirability and bring in the other two lenses later. Wicked problems demand teams to think outside the box, take action immediately, and constantly iterate—all hallmarks of design thinking. Use insights pulled from user research to identify user needs and challenges. While Design Thinking is often described as a mindset, at it’s core it is a five step process. Once you have defined your problem to solve, you can begin to explore ‘How Might We…’ statements. To begin with, you simply want to explore all possible options — to spark ideation and innovative, blue-sky thinking.
Get the mindset, the confidence and the skills that make UX designers so valuable. Build your UX career with a globally-recognised, industry-approved certification. IDEO took that idea and ran with it, creating Moonrise, an app that matches people looking for work with extra hours and income. Today’s businesses depend on on-demand work but the temp agencies they work with tend to want permanent placements.
At this stage, though, after you have spent time developing a heightened sense of what your users think and feel, you want to capture as many insights, suggestions, and potential product ideas as you can. The core advantage of design thinking is to build new perspectives and solutions from a place they were not previously accessible. This is enabled by the creative and visual method of ideation, which is inherently different than other brainstorming and problem-solving strategies. Real decisions are made to determine if solutions are sustainable options or merely good in theory.
In contrast to traditional problem-solving, which is a linear process of identifying a problem and then brainstorming solutions, design thinking only works if it is iterative. It is less of a means to get to a single solution, and more of a way to continuously evolve your thinking and respond to consumer needs. This Test stage might also help go back and build a better prototype, come up with more ideas for your product’s next iteration, or even help you gain more empathy for your customers. Now it’s time to learn just how much empathy you’ve gained for your target users, and how well the solution you built is resonating with those people. You will use this statement as the basis to begin developing ideas for products, services, or specific functionality, which you’ll do in the next step.
This contrasts with a more scientific approach where the concrete and known aspects are tested in order to arrive at a solution. It combines investigations into ambiguous elements of the problem with rational and analytical research—the scientific side in other words. This magical concoction reveals previously unknown parameters and helps to uncover alternative strategies which lead to truly innovative solutions.
The observations must happen with empathy, which means withholding judgment and not imparting preconceived notions of what the consumer needs. Observing with empathy is powerful because it can uncover issues the consumer didn’t even know they had or that they could not themselves verbalize. From this point, it’s easier to understand the human need for which you are designing.

No comments:
Post a Comment